Heart attack vs Cardiac Arrest – what is the difference?
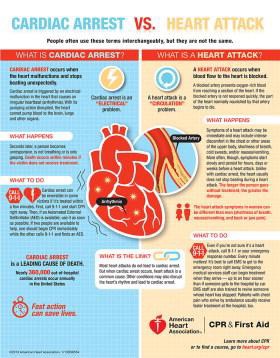
We hear the very tragic story of a young star athlete who was playing sports and collapsed suddenly on the field and died, or died in sleep without any knowledge for any medical problems. Most often, these cases are caused by sudden cardiac arrest. People often use these terms interchangeably, but they are not synonyms. A heart attack is when blood flow to the heart is blocked, and sudden cardiac arrest is when the heart malfunctions and suddenly stops beating unexpectedly. A heart attack is a “circulation” problem and sudden cardiac arrest is an “electrical” problem.
What is a heart attack?
A heart attack occurs when a blocked artery prevents oxygen-rich blood from reaching a section of the heart. If the blocked artery is not reopened quickly, the part of the heart normally nourished by that artery begins to die. The longer a person goes without treatment, the greater the damage. Symptoms of a heart attack may be immediate and intense. More often though, symptoms start slowly and persist for hours, days or weeks before a heart attack. Unlike with sudden cardiac arrest, the heart usually does not stop beating during a heart attack. The heart attack symptoms in women can be different than men.
What is cardiac arrest?
Sudden cardiac arrest occurs suddenly and often without warning. It is triggered by an electrical malfunction in the heart that causes an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia). With its pumping action disrupted, the heart cannot pump blood to the brain, lungs and other organs. Seconds later, a person loses consciousness and has no pulse. Death occurs within minutes if the victim does not receive treatment.
True story
So about one year ago, I was “on-call” for the hospital, it was early in the morning, around 7am, when a friend of mine called from the airplane – the were boarded and just about to take off when a passenger slumped over beside his wife. She immediately called for help and it was noted that the passenger was not responsive. Fortunately a doctor was on the flight and jumped into action quickly starting to provide hands-only CPR. My friend called me, not knowing I was on call, but she was shaken up by what had happened and just wanted to talk. After listening, I told her I’m going to go, because I’m pretty sure in they will be calling from the emergency room (ER) soon about this man… no sooner than I said that – my emergency phone beeped.
When I got to the ER, it turns out the passenger had a massive heart attack which then led to a cardiac arrest. So sometimes the two can be linked, but they are not one in the same. Most of the times when you hear of athletes, or some other young person without any known medical history collapsing and dying suddenly – it is usually because of a cardiac arrest – because the heart has gone into an abnormal rhythm, and not a heart attack.
What is the link?
These two distinct heart conditions are linked. Sudden cardiac arrest can occur after a heart attack, or during recovery. Heart attacks increase the risk for sudden cardiac arrest. Most heart attacks do not lead to sudden cardiac arrest. But when sudden cardiac arrest occurs, heart attack is a common cause. Other heart conditions may also disrupt the heart’s rhythm and lead to sudden cardiac arrest. These include a thickened heart muscle (cardiomyopathy), heart failure, arrhythmias, particularly ventricular fibrillation, and long Q-T syndrome.
Fast action can save lives. Find out what to do if someone experiences a heart attack or cardiac arrest.
What to do: Heart Attack
Even if you’re not sure it’s a heart attack, call for HELP or 119. . Every minute matters! It’s best to call an ambulance with trained emergency technicians to get to the emergency room right away. Emergency medical services staff can begin treatment when they arrive — up to an hour sooner than if someone gets to the hospital by car. Ambulance staff are also trained to revive someone whose heart has stopped. Patients with chest pain who arrive by ambulance usually receive faster treatment at the hospital, too.
What to do: Sudden Cardiac Arrest
Cardiac arrest is reversible in most victims if it’s treated within a few minutes. First, call for HELP or 119 for emergency medical services. Then get an automated external defibrillator if one is available and use it as soon as it arrives. Begin CPR immediately and continue until professional emergency medical services arrive. If two people are available to help, one should begin CPR immediately while the other calls 119 and finds an AED.
Sudden cardiac arrest is a leading cause of death – over 320,000 out-of-hospital cardiac arrests occur annually in the United States. By performing Hands-Only CPR to the beat of the classic disco song “Staying Alive,” you can double or even triple a victim’s chance of survival.
Learn Basic CPR
The Heart Foundation of Jamaica and other heart clinics offer Basic CPR, sign up today! and get certified. This is especially recommended if you have a relative or friend with a known heart problem.

